UP Demographics – UP Census 2011
UP Demographics UP Census 2011
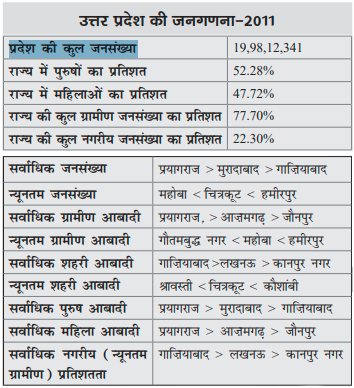
UP Demographics UP Census 2011
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. It contains less than 2% carbon and 1% manganese. It also contains little amount of silicon, phosphorus, sulphur and oxygen. India is the second largest steel producing country in the world after China. First Steel plant in India was the “Bengal Iron Works Company” at Kulthi near…
भारत में 23 ऑयल रिफाइनरी ( oil refineries in India in Hindi )हैं। 23 रिफाइनरी में से 18 रिफाइनरी पब्लिक सेक्टर की, 3 रिफाइनरी प्राइवेट सेक्टर की और 2 रिफाइनरी जाइंट सेक्टर की हैं। Oil Refineries in India in Hindi भारत में ऑयल रिफाइनरी 1. पारादीप रिफाइनरी (इंडियन ऑयल) 2. हल्दिया रिफाइनरी (इंडियन ऑयल) 3….
इस पोस्ट में भारत के प्रमुख बाँध एवं नदी परियोजनाएँ तथा वे किस नदी और राज्य से संबंधित हैं बताया गया है। भारत के प्रमुख बाँध एवं नदी परियोजनाएँ Major River Valley Project in Hindi इडुक्की परियोजना (Idukki Dam) – पेरियार नदी (Periyar River),केरल (Kerala) उकाई परियोजना (Ukai Project) – ताप्ती नदी (Tapi river), गुुजरात…
In this following section of Geography MCQ Exercise for SSC, UPSC, UPPSC and other competitive exams, 30 questions (MCQ) with 4 choices are given. Choose the right answer for each question. Answer of these Geography MCQ are available in the last of this post. Check how many of your answers are correct. Geography MCQ Exercise…