Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs also known as Maslow’s Theory of Motivation states that man’s behaviour is controlled by both internal and external motivational factors which he calls ‘needs’. He described that some needs are more basic or more powerful than other and as the needs are satisfied, other higher needs emerge. Maslow classified needs into two categories:-
- Basic Needs
- Growth Needs
Read – Piaget Theory of Cognitive Development
Basic Needs
As per Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs, Basic Needs are as following:-
- Physiological: The needs for body as sleep and rest, food, sex, shelter, drink and oxygen.
- Safety: The needs for safety, sense of stability and security.
Growth Needs
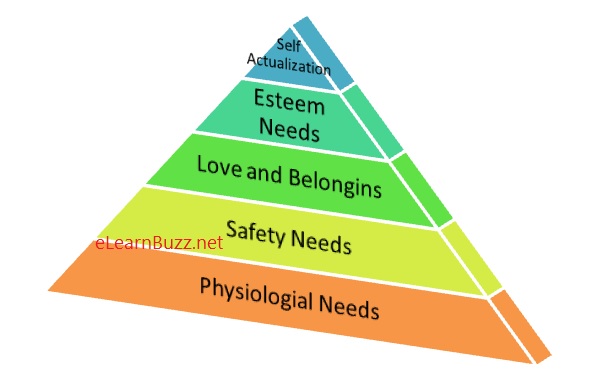
As per Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs, Growth Needs are as following:-
- Love and belonging: The need for love, affection, relationship, and care.
- Esteem: The need for self-respect, confidence, mastery, achievement, competence, respect from others, acceptance, reputation, recognition, status and prestige.
- Understanding and Knowledge: The need for exploring, discover, finding solution, meaning, satisfying curiosity, seek intellectual challenges.
- Aesthetics: The need for beauty in the surroundings.
- Self-Actualization: The need for growth and development, achieving desires, self fulfillment, utilization of potential.
You may use ‘comment section’ below for your valuable comments/feedback.
